Fibre optics
Fast networking, without trenches - cost-efficient and environmentally friendly
A high-performance and comprehensive fibre optic network is the backbone of digitisation. However, high costs and long construction times often act as a brake on investment in grid expansion, which is not progressing fast enough in many places. Trenchless technology shows that this need not be the case. Whether backbone or last mile, it can be used to lay fibre optic cables and establish fibre optic connections - without high costs and lengthy civil engineering work.
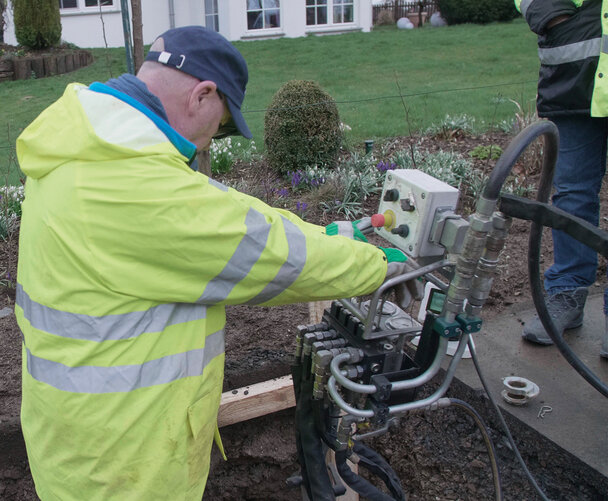

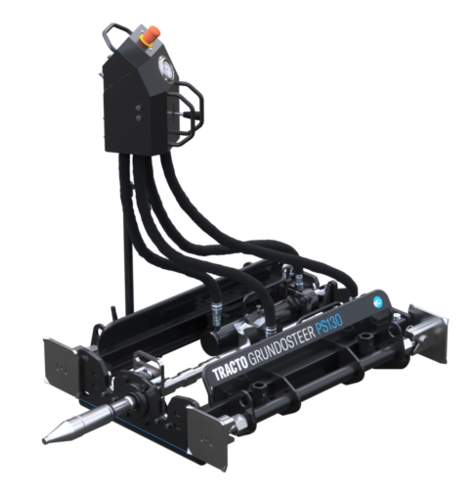
Our intelligent NODIG systems ensure rapid expansion by laying the protection pipes and fibre optic cables underground - right up to the connection at the end customer (FFTX), directly into the basement. Without follow-up costs, this ensures satisfied clients and customers.
Fibre optic expansion (FTTX) without time-consuming restoration work
Minimally invasive procedures using trenchless technology protect surfaces and avoid time-consuming and costly civil engineering work. There is no need to cut deep slots in the asphalt, so that the reduction in the value of affected areas and the restoration costs incurred remain particularly low. Fast and secure, the fibre optic cables can be installed underneath and alongside roads (FTTC), the house connections (FTTH) or fibre optic cables directly into the basement. Sufficient installation depths guarantee security of supply.
The perfect partner for your fibre optic project - all the advantages of expansion with NODIG systems
- Fast and minimally invasive installation of underground pipes and fibre optic cables alongside roads (FTTC) and underneath roads.
- Laying the fibre optic cables through existing sewers is also possible, which significantly reduces the restriction of residents or traffic infrastructure.
- Whether urban or rural - trenchless technology offers flexible deployment for fibre roll-out in the countryside to distribution and home connection in the city centre.
- All fibre optic connection variants (FTTX) are possible – The manufacture of individual or serial fibre optic house connections from the distributor to the building (FTTH) and directly into the basement (FTTB), or in the reverse direction as appropriate.
- The tried-and-tested processes are safe to use and, with perfectly matched accessories, offer maximum speed and economy.